تاریخ بروزرسانی(Update Date): 2nd November 2024
Introduction
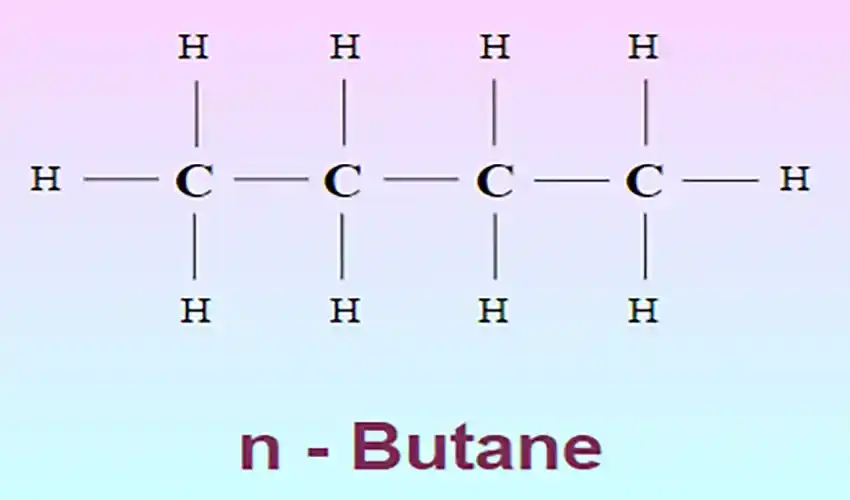
Normal butane is a linear isomer of butane with the molecular formula C4H10. This gas, with its unique characteristics, holds a special place in various industries. In this article, we aim to comprehensively examine normal butane and explore its different aspects in detail. From the production and extraction processes to its effects on human health, we will delve into the various dimensions of this widely used isomer.
Is there a difference between normal butane and butane?
When referring to “butane,” it may generally indicate a mixture of both isomers (normal butane and isobutane). However, to be more precise, “normal butane” specifically refers to one of these isomers. In other words, normal butane is a particular type of butane with a linear structure.
Methods of Producing Normal Butane
- Separation from Natural Gas
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane but also contains heavier hydrocarbons like ethane, propane, and butane. To separate these gases, natural gas is first dried to remove moisture. Then, through distillation and absorption processes, these valuable hydrocarbons are carefully separated.
- Separation from Crude Oil
In the process of refining crude oil, normal butane is separated as one of the lighter components through atmospheric distillation. In this process, crude oil is heated to high temperatures, and based on the boiling points of various components, it is separated in a distillation tower. Lighter components, such as normal butane, which have lower boiling points, are vaporized and extracted from the top of the distillation tower. After separation, normal butane undergoes additional refining processes to remove impurities. - Cracking
Cracking is a process in which heavier hydrocarbons like naphtha are converted into lighter hydrocarbons such as normal butane. This process is carried out using two main methods: thermal cracking, which uses high heat to break down molecules, and catalytic cracking, where catalysts help break larger molecules into smaller, more valuable components. - Isomerization
Isomerization is a process in which one molecule is converted into its isomer. Regarding normal butane, during the isomerization process, isobutane is converted into normal butane. However, this type of conversion is not widely used in the industry and is more common in research applications.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Normal Butane
Property | Value |
Chemical Formula | C₄H₁₀ |
Molar Mass | 58.12 g/mol |
Boiling Point | -0.5°C |
Melting Point | -138.4°C |
Flash Point | -60°C |
Enthalpy of Combustion | 2877 kJ/mol |
Solubility in Water | Very low |
Note: The data in the table corresponds to conditions at one atmosphere of pressure.Key Applications of Normal Butane
Key Applications of Normal Butane

- Used as fuel in lighters and portable stoves
- Serves as one of the components of LPG (liquefied petroleum gas)
- Used as a petrochemical feedstock for the production of chemicals such as butadiene and isobutene
Transportation of Normal Butane
Normal butane is primarily transported in a mixture with propane and isobutane in specialized LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) tankers. This mixture is commonly known as LPG due to the similar physical and chemical properties of these gases, allowing them to be blended and transported together. LPG tankers are designed to safely transport pressurized gases such as normal butane, propane, and isobutane. These tankers are typically equipped with advanced safety systems, including safety valves, pressure control systems, and special equipment to prevent gas leaks. In addition to LPG tankers, normal butane can also be transported in smaller steel cylinders for household and industrial use.
Normal Butane and Human Health
Inhaling normal butane gas can quickly lead to drowsiness, dizziness, and a temporary sense of euphoria. However, prolonged or continued inhalation poses more serious risks, such as heart problems, including arrhythmias and even cardiac arrest. Additionally, normal butane can negatively affect the central nervous system, potentially causing cognitive issues and memory impairments. Therefore, workers who come into contact with this gas must receive proper training and strictly follow safety protocols to prevent potential hazards. Maintaining awareness and implementing safety measures is essential not only for individual health but also for the overall safety of the workplace environment.
Hazards of Normal Butane

- High Flammability: Normal butane is highly flammable and should not be exposed to open flames, sparks, or heat sources. Containers or cylinders containing normal butane must be stored away from heat sources in cool, well-ventilated areas.
- Explosion Risk: When mixed with air in specific concentrations (1.8% to 8.4%), normal butane can create explosive mixtures. To prevent this risk, gas leaks must be avoided, and proper fire suppression and warning systems should be installed in areas where normal butane is stored or used.
- Asphyxiation Hazard: Normal butane is heavier than air and can accumulate in lower areas if leaked, increasing the risk of asphyxiation in confined spaces. In case of a gas leak, the area should be ventilated immediately, and people should be evacuated from the danger zone.
- Leakage Risk: Connections and equipment related to the storage and transfer of normal butane should be regularly inspected to prevent leaks. Safety equipment such as automatic shutoff valves and gas detectors can help prevent accidents.
Safety Precautions
- Use of Spark-Proof Equipment: Electrical and electronic devices used in environments containing normal butane must be explosion-proof and spark-proof.
- Avoid Fire Sources: Smoking, sparks, and any open flames must be kept away from areas where butane is stored or used.
- Proper Ventilation: Adequate ventilation systems should be installed in areas where butane is stored or used to prevent the accumulation of gas.
- Temperature Control: The temperature of storage tanks should be monitored to prevent excessive pressure buildup. Storing at appropriate temperatures (typically below 50°C) is essential.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Workers: All personnel should wear personal protective equipment, such as spark-resistant clothing, gloves, and safety goggles.
- Emergency Plan: Every workplace that stores or uses normal butane must have an emergency plan in place for gas leaks or fire incidents.
Final Word
Normal butane is one of the isomers of butane, extracted as a hydrocarbon gas from key sources like oil and natural gas, and has various production methods. It is typically transported as a liquid under pressure to ensure optimal and safe storage and handling. Given its effects on human health, including the high risks of flammability and asphyxiation if released in confined spaces, it is essential for all personnel to be fully familiar with the properties of this gas. Adhering to safety precautions when working with normal butane is crucial to prevent potential accidents and maintain a safe working environment.